Python Set Methods 🐍
#pythontips #pythonprogramming #pythonforbeginner
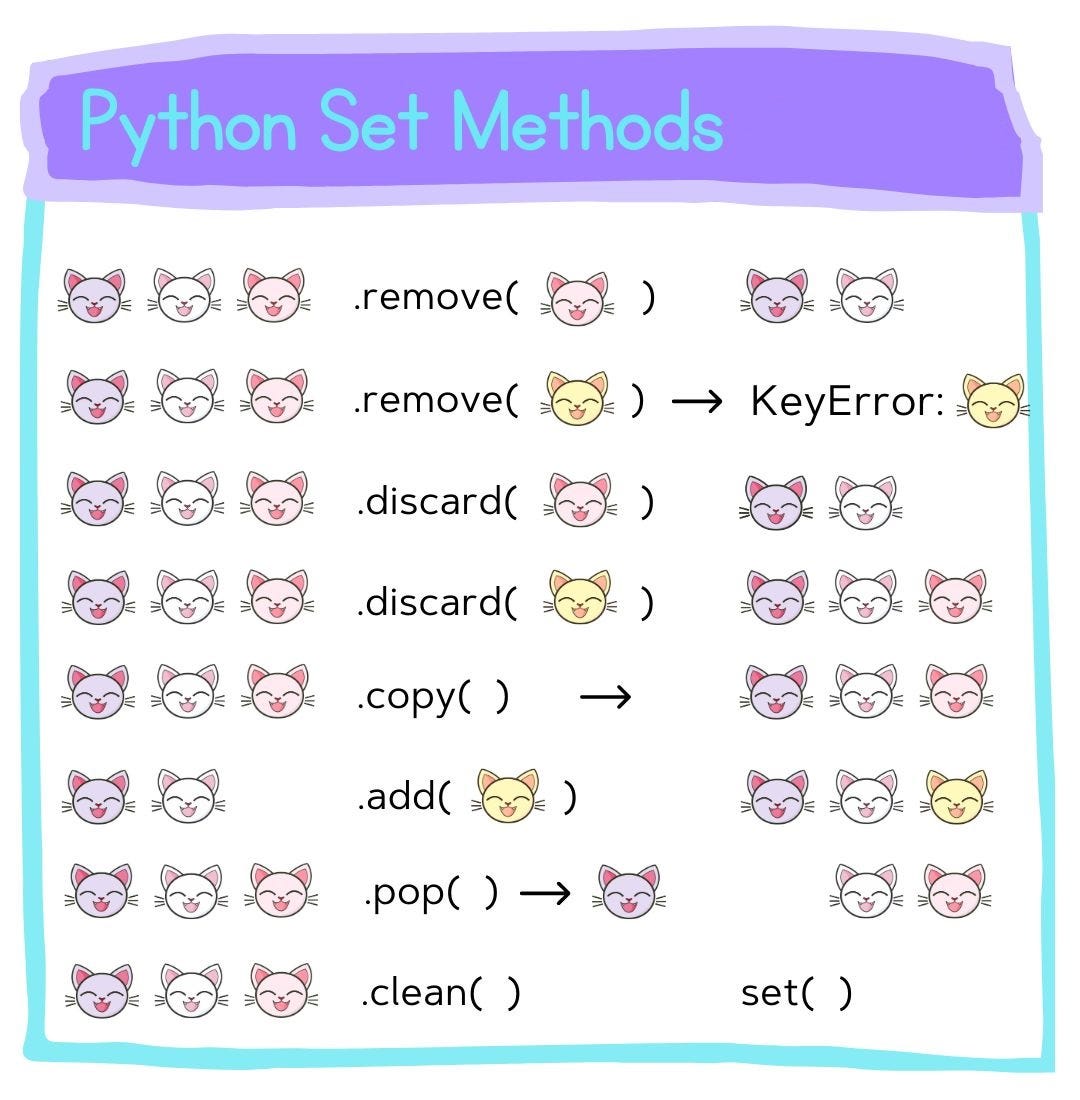
Python sets are unordered collections of unique elements. They provide a variety of built-in methods for performing operations on sets. Here are some commonly used Python set methods:
add(): Adds an element to the set.remove(): Removes a specified element from the set. Raises an error if the element is not found.discard(): Removes a specified element from the set if it exists. Does not raise an error if the element is not found.pop(): Removes and returns an arbitrary element from the set.clear(): Removes all elements from the set.copy(): Creates a shallow copy of the set.union(): Returns a new set that is the union of the current set and another set or iterable.intersection(): Returns a new set that is the intersection of the current set and another set or iterable.difference(): Returns a new set that contains elements present in the current set but not in another set or iterable.symmetric_difference(): Returns a new set that contains elements that are present in either the current set or another set, but not both.issubset(): Checks if the current set is a subset of another set.issuperset(): Checks if the current set is a superset of another set.isdisjoint(): Checks if the current set has no common elements with another set.